4 min read
Nginx, Loki, Promtail and Grafana
Hey devops engineer, you don’t need Logtail, Sentry, Datadog or any other SaaS/PaaS service to manage your logs. Collecting and analyzing log files is super easy with the LPG-stack. Another acronym that stands for Loki, Promtail and Grafana.
I will give you a brief overview of how you can deploy the LPG-stack and label your log entries with Promtail. To sum it up we will have look at Grafana and see how we can query the log data
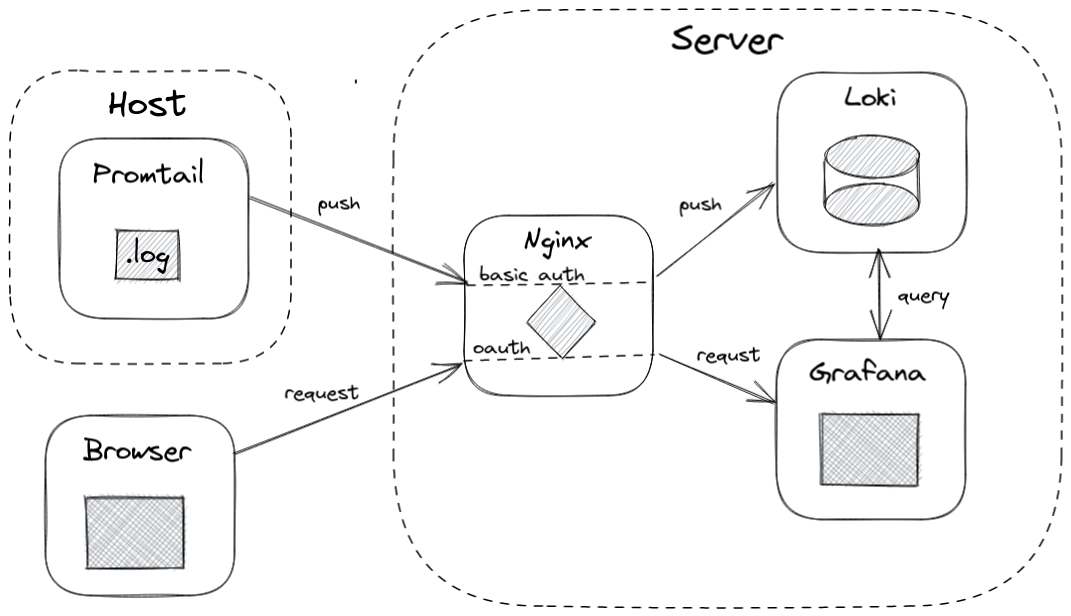
Usually you would follow these four steps to setup the log monitoring system:
- Setup loki for indexing log data
- Setup nginx reverse proxy to expose loki with basic auth
- Configure promtail and forward logs on host
- Create a dashboard in grafana and query the data
However, giving details on the full setup would make this post unnecessarily long. That is why I added a note Not covered: note to every section. The deployment of these services depends heavily on the technology (f.g. Kubernetes, Docker Compose or Ansible) you are using. I will fokus on the most important part - the config files.
Loki
Not covered: Deployment and configuration of the Loki container.
Loki manages the log index. It receives the log files from Promtail and acts as a datasource for Grafana.
The configuration below is based on the official template and has not been altered notably.
local-config.yml
# https://github.com/grafana/loki/blob/v2.3.0/cmd/loki/loki-local-config.yaml
auth_enabled: false
server:
http_listen_port: 3100
grpc_listen_port: 9096
ingester:
wal:
enabled: true
dir: /tmp/wal
lifecycler:
address: 127.0.0.1
ring:
kvstore:
store: inmemory
replication_factor: 1
final_sleep: 0s
chunk_idle_period: 1h # Any chunk not receiving new logs in this time will be flushed
max_chunk_age: 1h # All chunks will be flushed when they hit this age, default is 1h
chunk_target_size: 1048576 # Loki will attempt to build chunks up to 1.5MB, flushing first if chunk_idle_period or max_chunk_age is reached first
chunk_retain_period: 30s # Must be greater than index read cache TTL if using an index cache (Default index read cache TTL is 5m)
max_transfer_retries: 0 # Chunk transfers disabled
schema_config:
configs:
- from: 2020-10-24
store: boltdb-shipper
object_store: filesystem
schema: v11
index:
prefix: index_
period: 24h
storage_config:
boltdb_shipper:
active_index_directory: /tmp/loki/boltdb-shipper-active
cache_location: /tmp/loki/boltdb-shipper-cache
cache_ttl: 24h # Can be increased for faster performance over longer query periods, uses more disk space
shared_store: filesystem
filesystem:
directory: /tmp/loki/chunks
compactor:
working_directory: /tmp/loki/boltdb-shipper-compactor
shared_store: filesystem
limits_config:
reject_old_samples: true
reject_old_samples_max_age: 168h
chunk_store_config:
max_look_back_period: 0s
table_manager:
retention_deletes_enabled: false
retention_period: 0s
ruler:
storage:
type: local
local:
directory: /tmp/loki/rules
rule_path: /tmp/loki/rules-temp
alertmanager_url: http://localhost:9093
ring:
kvstore:
store: inmemory
enable_api: true
Nginx reverse proxy
Not covered: Full nginx config with https server definition.
The Nginx proxy terminates https connections and ensures the connections to Loki are authenticated with basic auth.
The configuration below shows the proxy configuration for Loki.
loki.nginx
location /loki/api/v1 {
auth_basic "loki";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/conf.d/proxies/loki.htpasswd;
proxy_pass http://loki01:3100/loki/api/v1;
include /etc/letsencrypt/proxy-params.conf;
}
Promtail
Not covered: Deployment of the Promtail container.
Promtail has access to the log folder of the host machine. It extracts all log data and forwards the content to Loki.
Promtail has been configured to use basic auth and extract Docker log files. Before sending the log files it processes and labels the log lines.
config.yml
server:
http_listen_port: 9080
grpc_listen_port: 0
positions:
filename: /tmp/positions.yaml
clients:
- url: https://loki:ohs24234ch5vahz5ieVei@monitor.example.com/loki/api/v1/push
scrape_configs:
- job_name: containers
static_configs:
- targets:
- localhost
labels:
job: containerlogs
instance: server.example.com
__path__: /var/lib/docker/containers/*/*log
pipeline_stages:
- json:
expressions:
output: log
stream: stream
attrs:
- json:
expressions:
tag:
source: attrs
- regex:
expression: (?P<container_name>(?:[^|]*[^|])).(?P<image_name>(?:[^|]*[^|]))
source: tag
- timestamp:
format: RFC3339Nano
source: time
- labels:
#tag:
stream:
container_name:
image_name:
- output:
source: output
Ensure docker containers are deployed with these log options:
"LogConfig": {
"Type": "json-file",
"Config": {
"max-file": "3",
"max-size": "10m",
"tag": "nginx03|nginx"
}
},
Grafana
Not covered: Deployment of the Grafana container.
Grafana is our monitoring tool. It visualizes the data from Loki. Getting the data requires settings up a data source.
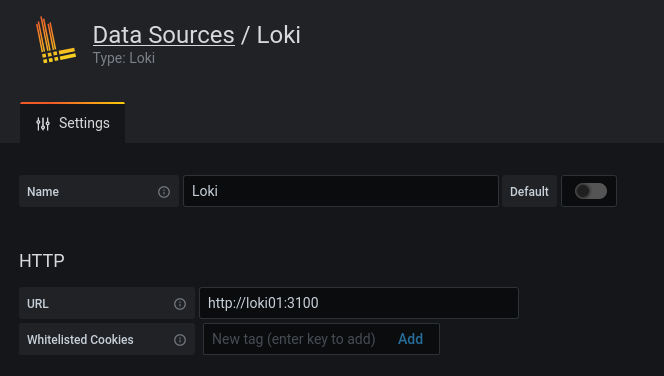
If the connection is private, there is no need for authentication.
In the Grafana data explorer the log data can be queried:
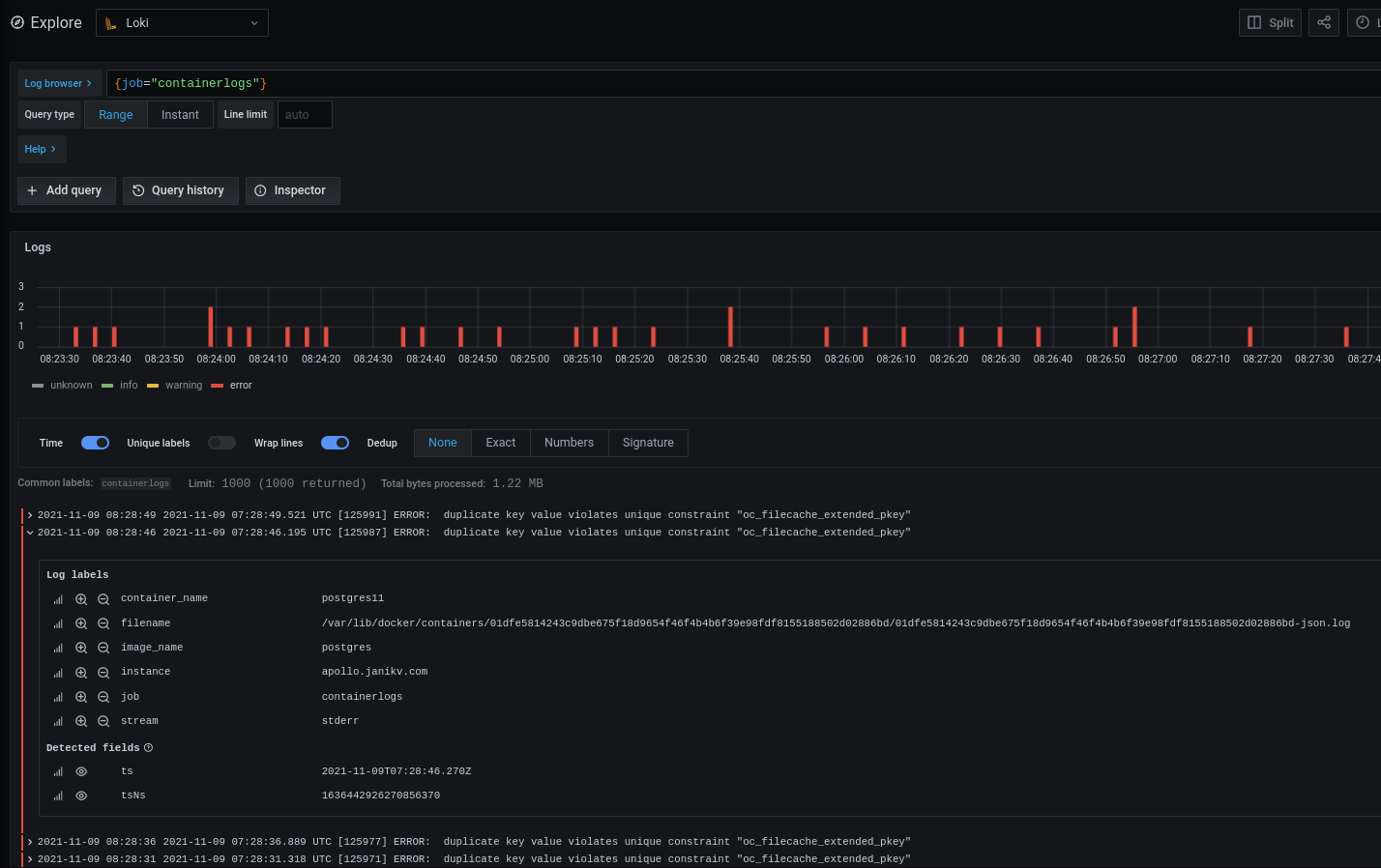
With queries like rate(({job="containerlogs"} |= "error")[1m]) the frequency of errors within a time range will be returned.
Finally, you could setup an alert for a certain threshold on the frequency quer.
Categories: System EngineeringTags: grafana , loki , promtail , nginx , devops
Edit this page
Show statistic for this page