
10 min read
SQL Cheat Sheet
You can get the latest version of this SQL cheat sheet here: https://gist.github.com/janikvonrotz/6e27788f662fcdbba3fb
SQL languages
DDL is short name of Data Definition Language, which deals with database schemas and descriptions, of how the data should reside in the database.
DML is short name of Data Manipulation Language which deals with data manipulation, and includes most common SQL statements such SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE etc, and it is used to store, modify, retrieve, delete and update data in database.
DCL is short name of Data Control Language which includes commands such as GRANT, and mostly concerned with rights, permissions and other controls of the database system.
Datatypes
Text types
| Data type | Description |
|---|---|
| CHAR(size) | Holds a fixed length string (can contain letters, numbers, and special characters). The fixed size is specified in parenthesis. Can store up to 255 characters |
| VARCHAR(size) | Holds a variable length string (can contain letters, numbers, and special characters). The maximum size is specified in parenthesis. Can store up to 255 characters. Note: If you put a greater value than 255 it will be converted to a TEXT type |
| TINYTEXT | Holds a string with a maximum length of 255 characters |
| TEXT | Holds a string with a maximum length of 65,535 characters |
| BLOB | For BLOBs (Binary Large OBjects). Holds up to 65,535 bytes of data |
| MEDIUMTEXT | Holds a string with a maximum length of 16,777,215 characters |
| MEDIUMBLOB | For BLOBs (Binary Large OBjects). Holds up to 16,777,215 bytes of data |
| LONGTEXT | Holds a string with a maximum length of 4,294,967,295 characters |
| LONGBLOB | For BLOBs (Binary Large OBjects). Holds up to 4,294,967,295 bytes of data |
| ENUM(x,y,z,etc.) | Let you enter a list of possible values. You can list up to 65535 values in an ENUM list. If a value is inserted that is not in the list, a blank value will be inserted.Note: The values are sorted in the order you enter them.You enter the possible values in this format: ENUM(‘X’,‘Y’,‘Z’) |
| SET | Similar to ENUM except that SET may contain up to 64 list items and can store more than one choice |
Number types
| Data type | Description |
|---|---|
| TINYINT(size) | -128 to 127 normal. 0 to 255 UNSIGNED*. The maximum number of digits may be specified in parenthesis |
| SMALLINT(size) | -32768 to 32767 normal. 0 to 65535 UNSIGNED*. The maximum number of digits may be specified in parenthesis |
| MEDIUMINT(size) | -8388608 to 8388607 normal. 0 to 16777215 UNSIGNED*. The maximum number of digits may be specified in parenthesis |
| INT(size) | -2147483648 to 2147483647 normal. 0 to 4294967295 UNSIGNED*. The maximum number of digits may be specified in parenthesis |
| BIGINT(size) | -9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807 normal. 0 to 18446744073709551615 UNSIGNED*. The maximum number of digits may be specified in parenthesis |
| FLOAT(size,d) | A small number with a floating decimal point. The maximum number of digits may be specified in the size parameter. The maximum number of digits to the right of the decimal point is specified in the d parameter |
| DOUBLE(size,d) | A large number with a floating decimal point. The maximum number of digits may be specified in the size parameter. The maximum number of digits to the right of the decimal point is specified in the d parameter |
| DECIMAL(size,d) | A DOUBLE stored as a string , allowing for a fixed decimal point. The maximum number of digits may be specified in the size parameter. The maximum number of digits to the right of the decimal point is specified in the d parameter |
Date types
| Data type | Description |
|---|---|
| DATE() | A date. Format: YYYY-MM-DDNote: The supported range is from ‘1000-01-01’ to ‘9999-12-31’ |
| DATETIME() | *A date and time combination. Format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SSNote: The supported range is from ‘1000-01-01 00:00:00’ to ‘9999-12-31 23:59:59’ |
| TIMESTAMP() | *A timestamp. TIMESTAMP values are stored as the number of seconds since the Unix epoch (‘1970-01-01 00:00:00’ UTC). Format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SSNote: The supported range is from ‘1970-01-01 00:00:01’ UTC to ‘2038-01-09 03:14:07’ UTC |
| TIME() | A time. Format: HH:MI:SSNote: The supported range is from ‘-838:59:59’ to ‘838:59:59’ |
| YEAR() | A year in two-digit or four-digit format.Note: Values allowed in four-digit format: 1901 to 2155. Values allowed in two-digit format: 70 to 69, representing years from 1970 to 2069 |
Database
Create
create database dbname;
Drop
drop database dbname;
Table
Check if not exit and create
IF OBJECT_ID('tbl_kunde', N'U') is not null
drop table tbl_kunde;
GO
create table tbl_kunde (
id_kunde int not null primary key,
fi_moral_nr int,
name varchar(25) not null,
vorname varchar not null,
wohnort varchar
);
GO
Alter Table
Primary Key
ALTER TABLE tbl_kunde ADD PRIMARY KEY (id_kunde);
Foreign Key
ALTER TABLE tbl_kunde ADD CONSTRAINT FK_fi_moral_nr FOREIGN KEY (fi_moral_nr)
REFERENCES tkey_moral
ON UPDATE CASCADE
ON DELETE SET NULL;
Constraint
ALTER TABLE tkey_moral ADD CONSTRAINT PK_id_moral_nr PRIMARY KEY (id_moral_nr);
ALTER TABLE tbl_kunde ADD CONSTRAINT FK_fi_moral_nr FOREIGN KEY (fi_moral_nr)
REFERENCES tkey_moral
ON UPDATE CASCADE
ON DELETE SET NULL;
Insert
Selected fields
insert into tkey_moral (id_moral_nr, moral_bez) values (1, 'gut'), (2, 'schlecht'), (3, 'schlecht');
All fields
INSERT INTO tbl_kunde VALUES (3838,1,'Meier','Laura','Waldibrücke')
Update
Update by condition
update tbl_kunde set name = 'Menzer' where name = 'Waltenspühl-Menzer'
update tass_police set praem_stufe = 101 where praem_stufe = 108
Delete
All
delete from tbl_kunde
Condition
delete from tkey_moral where id_moral_nr = 4
delete from tbl_kunde where vorname = 'Peter' and name = 'Fischer' or vorname = 'Martin' and name = 'Müller'
Index
Create
create unique index ix_kund_name on tbl_kunde (name)
Disable
alter index ix_kund_name on tbl_kunde disable
Rebuild
alter index ix_kund_name on tbl_kunde rebuild
Reorganize
alter index ix_kund_name on tbl_kunde reorganize
Drop
drop index ix_kund_name on tbl_kunde
Alter
drop index ix_kund_name on tbl_kunde
Type
create
create type tp_moralisches from numeric(9,0)
Login
change password
alter login stud23 with password = 'hello' old_password = 'pass_wd23'
User
create
create user romulus from login romulus
drop
drop user romulus
Grant/ Revoke
Available permissions: CREATE DEFAULT, CREATE FUNCTION, CREATE PROCEDURE, CREATE ROLE, CREATE TABLE, CREATE TYPE, CREATE VIEW, DELETE, EXECUTE, INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE
Grant rights
grant select, insert, delete, references, update to romulus
Grant refrences
grant references (id_moral_nr) on tkey_moral to romulus
Revoke
revoke insert, delete, references, update to romulus
Role
Create
create role verkauf
Add member
exec sp_addrolemember 'verkauf', 'anna'
Grant Role
Grant rights
grant select, update, insert, delete on tbl_kunde to verkauf
View
Create detailed
CREATE VIEW v_kunden (id, name, vorname, ort, police, gebiet) AS
SELECT k.id_kunde, k.name, k.vorname, k.wohnort, v.vers_bez,
v.vers_gebiet
FROM tbl_kunde AS k, tkey_versicherung AS v, tass_police AS p
WHERE k.id_kunde = p.id_fi_kunde
AND p.id_fi_vers_art = v.id_vers_art;
Create simple
create view plain as select id_kunde, name, vorname from tbl_kunde
Create advanced
create view v_umsatz as select sum(cast(bezahlt as float)) as 'Umsatz aus Policen' from tass_police
Select
Basic
select dt_jahr from dbo.tbl_stueck
Condition
select dt_jahr from dbo.tbl_stueck where dt_jahr is not null
Order
select dt_jahr from dbo.tbl_stueck
where dt_jahr is not null
order by dt_jahr desc
Distinct
select distinct dt_jahr from dbo.tbl_stueck
where dt_jahr is not null
order by dt_jahr asc
And Condition
select * from tbl_stueck where dt_jahr = 1970 and dt_zeit > 3
Between
select * from tbl_stueck where dt_jahr = 1970 and dt_zeit between 3 and 10
Like
select * from tbl_stueck where dt_stueck_titel like 'Let%'
Count
select count(dt_stueck_titel) from tbl_stueck where dt_stueck_titel like 'Let%'
Having and without join
select i.dt_name, count(s.dt_stueck_titel) from tbl_stueck as s, tkey_interpret as i
where s.fi_interpret = i.id_interpret
group by i.dt_name
having count(s.dt_stueck_titel) >10
order by count(s.dt_stueck_titel) de
Join the hard way
Inner Join
select s.dt_stueck_titel, i.dt_name
from tbl_stueck as s, tkey_interpret as i
where s.fi_interpret = i.id_interpret
order by s.dt_stueck_titel
Multi Join
select sa.id_jahr, st.dt_stueck_titel, ip.dt_name
from tbl_stueck as st, tass_stueck_sampler as ss, tkey_sampler as sa, tkey_interpret as ip
where ss.id_fi_stueck_nr = st.id_stueck_nr
and ss.id_fi_jahr = sa.id_jahr
and st.fi_interpret = ip.id_interpret
order by st.dt_stueck_titel
Join the right way
Inner Equi Key Joining
select dt_stueck_titel, dt_name
from tbl_stueck join tkey_interpret
on fi_interpret = id_interpret
order by dt_stueck_titel
Multi Inner Equi Key Joining
select id_fi_jahr, dt_stueck_titel, dt_name
from tbl_stueck
join tass_stueck_sampler on id_fi_stueck_nr = id_stueck_nr
join tkey_interpret on fi_interpret = id_interpret
order by dt_stueck_titel
About Joins
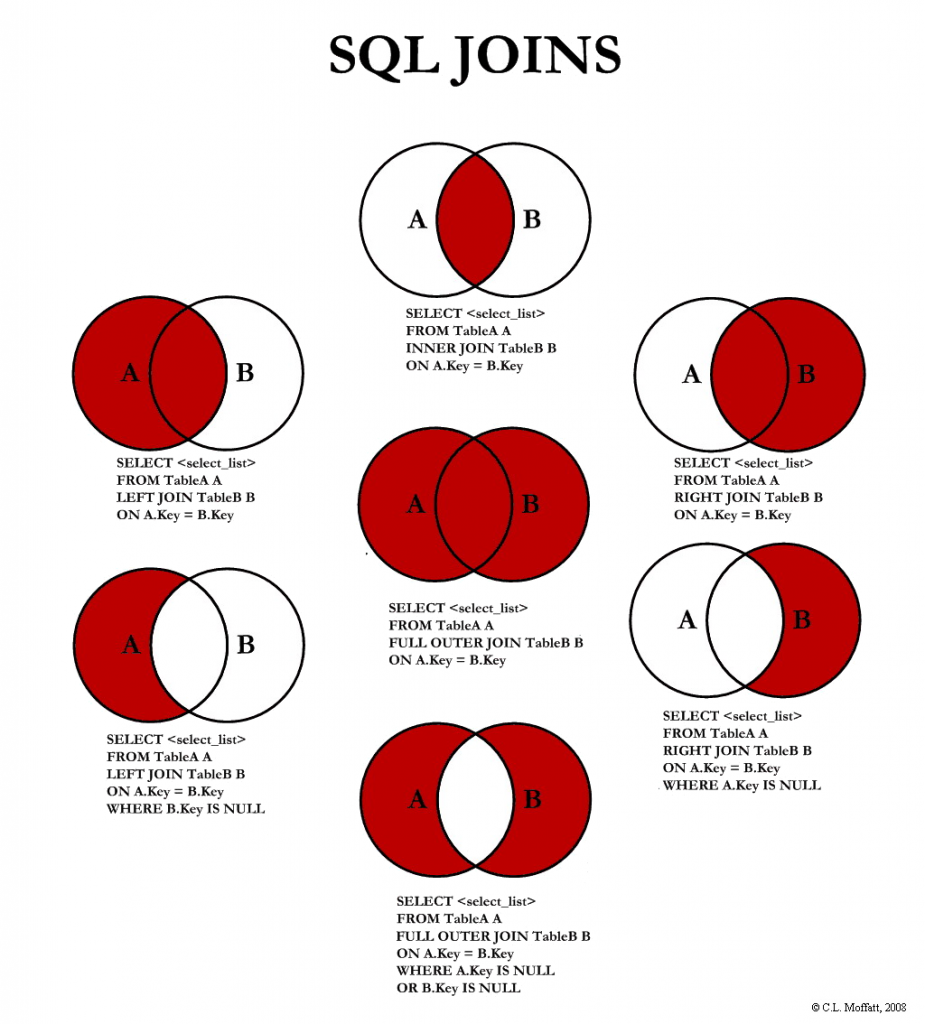 ![sql 1=“summary” language=“join”]/sql
![sql 1=“summary” language=“join”]/sql
SELECT customers.id, customers.name, items.name, customers.state
FROM customers, items
WHERE customers.id=seller_id
ORDER BY customers.id
Join tables -> Joining two tables together in a query output. The third line is important because it shows how the two tables are related (in this case it is their key values).
SELECT customers.name, items.name FROM customers
LEFT OUTER JOIN items ON customers.id=seller_id
LEFT/RIGHT OUTER JOIN -> Takes the table left of the word ‘LEFT’ or ‘RIGHT’ (in this case customers) and joins it regardless of whether it has any values or not. So the above statement shows all users/customers, even if they aren’t selling anything.
Select with Subqueries
Select max and min values
select dt_stueck_titel as Titel, dt_zeit as Zeit
from tbl_stueck
where dt_zeit = (select max(dt_zeit) from tbl_stueck)
or dt_zeit = (select min(dt_zeit) from tbl_stueck)
order by dt_zeit;
Select with query in condition
select dt_stueck_titel as Titel, dt_zeit as Zeit
from tbl_stueck
where dt_zeit between (select avg(dt_zeit) from tbl_stueck)*0.9
and (select avg(dt_zeit) from tbl_stueck)*1.1
order by dt_zeit;
Select query as value
select dt_stueck_titel as Titel,
dt_zeit/(select avg(dt_zeit) from tbl_stueck)*100 as Zeit
from tbl_stueck
where dt_stueck_titel = 'You Shook Me'
Union
Unify two result sets with a condition
select * from
(select dt_stueck_titel as titel, 'stück' as 'type' from tbl_stueck
union
select dt_name as titel, 'inter' as 'type' from tkey_interpret
union
select dt_stao as titel, 'stao' as 'type' from tkey_standort) as t
where t.titel like '%boy%'
Transactions
Run a transaction
begin transaction
update tass_police set bezahlt = 0 where id_fi_kunde = 3533 and id_fi_vers_art = 1700
commit
-- or rollback
Function
A function can be called from inside a statement just like any other function and can return a scalar value.
Create - Get value from table
create function f_plic_bez()
returns decimal(10,2)
as begin
return (select sum(bezahlt) from tass_police)
end;
go
select dbo.f_plic_bez() AS 'Summe aller bezahlten Leistungen'
go
Drop
drop function f_bezahlt_versich
Create - With parameters
create function f_rabatt(@name varchar(40), @vers varchar(30))
returns int
as begin
return (select (praem_stufe-100)*10 from tass_police
join tbl_kunde on id_fi_kunde = id_kunde
join tkey_versicherung on id_fi_vers_art = id_vers_art
where name = @name and vers_bez = @vers)
end
Procedure
Stored procedures are stored as precompilated code (stored routine) and called by the programmer wherever it wants to fire. Stored procedure can return value(s).
Create and execute
CREATE PROCEDURE p_polic_del @fname VARCHAR(30), @versich VARCHAR(30)
AS
BEGIN
DELETE FROM tass_police
FROM tbl_kunde, tkey_versicherung
WHERE name = @fname
AND id_kunde = id_fi_kunde
AND id_fi_vers_art = id_vers_art
AND vers_bez = @versich
IF @@ROWCOUNT = 0
PRINT 'Police existiert nicht.'
ELSE PRINT 'Löschung vollzogen.'
END
GO
EXECUTE p_polic_del 'Meier', 'Taggeld';
Variables
Declare
DECLARE @veraenderung SMALLINT = 180;
DECLARE @neue_summe INT;
Trigger
Triggers are named database objects fired automatically when insert, delete, update (or other event) occurred, there can be no explicit invocation. Trigger can not return any data.
Create simple
create trigger t_ort on tbl_kunde
after insert, update
as beginn
set @ort = select wohnort from inserted)
if((@ort like '/^[A-Z]') && len(@ort) < 2)
rollback transaction
end
end
Drop
drop trigger t_ort
Checks the referential integrity
create trigger t_bst_mut on bst
for insert, update
as
begin
set nocount on;
if(select id_fi_k from inserted) NOT IN (select id_kund from knd)
begin
raiserror('Es besteht kein entsprechender Kunde.', 15, 1);
rollback transaction;
end
end;
Replaces on delete no action
create trigger t_ku_del on knd
for delete
as
begin
set nocount on;
if((select id_kunde from deleted) IN (select id_fi_k from bst))
begin
raiserror('Löschung verwert; es bestehen noch Bestelungen für diesen Kunden.', 15, 1)
rollback transaction
end
end;
Replaces on update cascade
create trigger t_update_knd on knd
after update
as
begin
set nocount on;
update bst set id_fi_k = (select id_kund from inserted)
end;
Replaces on delete cascade
create trigger t_delete_knd on knd
after delete
as
begin
delete from bst where id_fi_k = (select id_kund from deleted)
end;
Tags: cheat sheet , function , procedure , transaction
Edit this page
Show statistic for this page