
3 min read
Build a Java 3-tier application from scratch – Part 5: Client controller
As you’ve seen there are 5 models in our application. This is not that much but requires a lot of effort to display them in the client application. As this tutorial doesn’t cover every aspect of a rich 3-tier applicatoin I will show only how you can authenticate the client application and edit the Employer entities.
As always we create our filestructure first. Make sure the client eclipse project looks like:
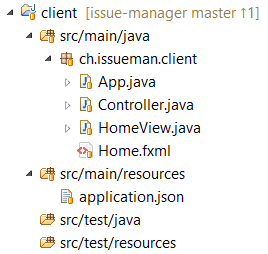
App
To launch the client application java requires a main method.
- Update the application launcher class.
App.java
package ch.issueman.client;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.fxml.FXMLLoader;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class App extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) {
try {
primaryStage.setResizable(false);
primaryStage.setTitle("Issue Manager");
primaryStage.setScene(new Scene(FXMLLoader.load(getClass().getResource("Home.fxml"))));
primaryStage.show();
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
We will define the view in the next chapter. Same as the webservice our client application load configurations from one json file.
- Update the configuration file.
application.json
{
"webservice": {
"url": "http://localhost:8080/webservice"
}
}
The only property as you can see is the webservice endpoint url. This is the jetty default address, do not change it unless you know whats going on.
Controller
controller.java
The client controller has the same functionality as the server controller. With the help of the RESTeasy client and the Jackson JSON mapper the controller communicates with the webservice and converts the JSON data to POJOs.
package ch.issueman.client;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ws.rs.client.Entity;
import javax.ws.rs.client.WebTarget;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response.Status;
import org.codehaus.jackson.map.ObjectMapper;
import org.codehaus.jackson.map.type.TypeFactory;
import org.jboss.resteasy.client.jaxrs.BasicAuthentication;
import org.jboss.resteasy.client.jaxrs.ResteasyClient;
import org.jboss.resteasy.client.jaxrs.ResteasyClientBuilder;
import com.typesafe.config.ConfigFactory;
import ch.issueman.common.DAO;
import ch.issueman.common.Model;
import ch.issueman.common.User;
public class Controller<T, Id extends Serializable> implements DAO<T, Id> {
private static ResteasyClient client = new ResteasyClientBuilder().build();
private String url;
private ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
private final Class<T> clazz;
private User user;
public Controller(Class<T> clazz, User user) {
this.clazz = clazz;
url = ConfigFactory.load().getString("webservice.url") + "/" + clazz.getSimpleName().toLowerCase();
this.user = user;
}
public boolean login(){
Boolean status = false;
try {
WebTarget target = client.target(ConfigFactory.load().getString("webservice.url") + "/login");
Response response = target.request(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).post(Entity.json(mapper.writeValueAsString(user)));
if(response.getStatus() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()){
user = mapper.readValue(response.readEntity(String.class), User.class);
client = new ResteasyClientBuilder().register(new BasicAuthentication(user.getEmail(), user.getPassword())).build();
status = true;
}
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return status;
}
public T getById(Id id) {
WebTarget target = client.target(url + "/" + id);
try {
Response response = target.request(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).get();
T t = mapper.readValue(response.readEntity(String.class), clazz);
response.close();
return t;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
public List<T> getAll() {
WebTarget target = client.target(url);
TypeFactory t = TypeFactory.defaultInstance();
try {
Response response = target.request(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).get();
List<T> l = mapper.readValue(response.readEntity(String.class), t.constructCollectionType(List.class,clazz));
response.close();
return l;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
@Override
public void persist(T t) {
WebTarget target = client.target(url);
try {
Response response = target.request(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).post(Entity.json(mapper.writeValueAsString(t)));
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void update(T t) {
try {
WebTarget target = client.target(url);
Response response = target.request(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).put(Entity.json(mapper.writeValueAsString(t)));
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void delete(T t) {
WebTarget target = client.target(url + "/" + ((Model)t).getId());
Response response = target.request(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).delete();
response.close();
}
@Override
public void deleteAll() {
}
}
In addition this controller has a login method. You can pass a user object and run this method to authenticate the controller against the webservice. Pretty easy, isn’t it?
See you in the next and last part when write the client view.
Links
- Part 1: Introduction and project setup
- Part 2: Model setup
- Part 3: Object-relational mapping
- Part 4: Webservice
- Part 5: Client controller
- Part 6: Client view
Tags: authentication , java , javafx , webservice
Edit this page
Show statistic for this page